Tailgating, also known as piggybacking, is a physical security breach that occurs when an unauthorized person follows an authorized individual into a restricted area without proper identification. Although tailgating is a physical security issue it is very much connected to cybersecurity as tailgating is one method used by cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive data and systems.
A breach of this type can result in significant financial consequences for organizations, including theft of property, loss of sensitive data, and damage to reputation. In a worst case scenario, a tailgating breach can even lead to the physical harm of employees, therefore minimizing the risk of tailgating is vitally important. So is understanding the potential cost of tailgating and how your organization can mitigate its financial impact.
Direct Costs of Tailgating
The direct costs of tailgating include the value of the stolen data or equipment. In some cases, tailgating can result in the loss of expensive equipment or intellectual property, leading to a significant financial burden on the organization. For example, if an unauthorized person gains access to a research lab and steals confidential research data or equipment, the cost of replacing or recovering the stolen items can be high.
Indirect Costs of Tailgating
The indirect costs of tailgating include the time and resources required to investigate the breach, repair the damage, and prevent similar incidents in the future. These costs can include hiring security personnel, implementing new security measures, and giving the right security training to employees. The indirect costs of tailgating can be substantial, and organizations should factor these costs into their overall security budget.

Reputation Damage
Tailgating can also damage an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and potential business opportunities. If an organization fails to protect its premises or data from unauthorized access, customers and investors may perceive the organization as untrustworthy, leading to a loss of revenue. Additionally, if the breach results in a public data leak or theft, the organization may face lawsuits or regulatory penalties, further damaging its reputation and finances.
Mitigating the Financial Impact of Tailgating
Organizations can mitigate the financial impact of tailgating by implementing a multi-layered security approach that includes physical barriers, access control systems, security personnel, and employee security training. Physical barriers such as turnstiles or access control gates can help prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to restricted areas. Access control systems such as biometric scanners or key cards can provide an additional layer of security by requiring proper identification before granting access. Additionally, security personnel can monitor entry points and challenge individuals who do not have proper identification.
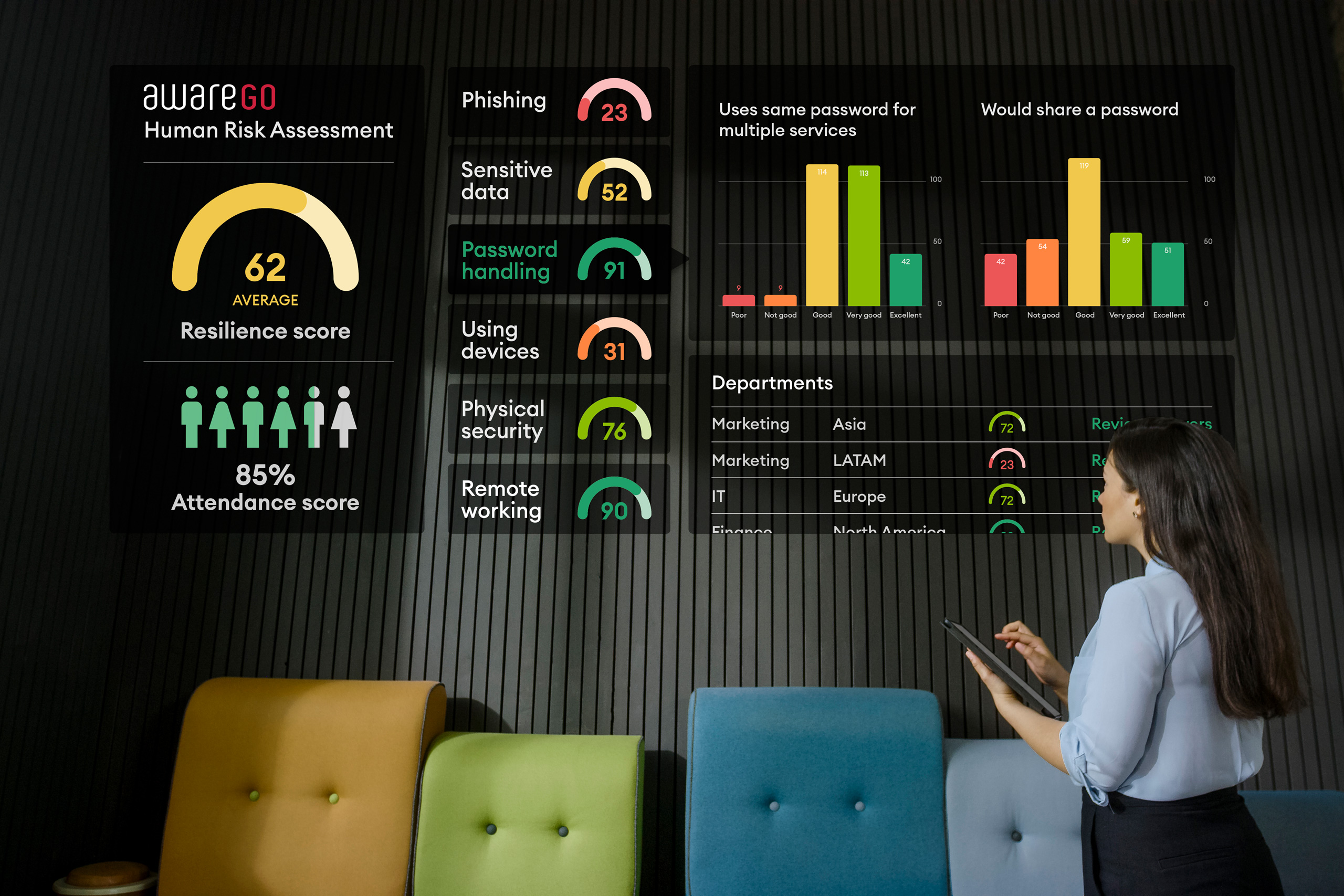
Employee training is essential to prevent tailgating. Employees should be trained on security protocols, including how to recognize and report suspicious behavior. AwareGO offers in-depth security awareness training on specific security issues curated to your organization’s needs. You can find out more about the type of security training that best fits your needs by having your employees take the Human Risk Assessment.
The financial impact of tailgating can be substantial, leading to direct and indirect costs, as well as damage to an organization’s reputation. To mitigate this risk, organizations should implement a multi-layered security approach and provide regular cyber security awareness training to employees. By doing so, organizations can reduce the likelihood of a security breach and minimize its financial impact.